Symbiotic binaries
A symbiotic binary consists of a mass-losing red giant
star and a hot, compact companion (typically a white-dwarf). The hot
star ionizes some of the material shed by the giant, and this leads to
the symbiotic's characterisitic composite spectrum of nebular emission
lines superimposed on molecular absorption bands. Symbiotic binaries
are valuable laboratories for the study of cool stellar winds, ionized
nebulae, wind-fed accretion processes and wind-wind collision
dynamics.
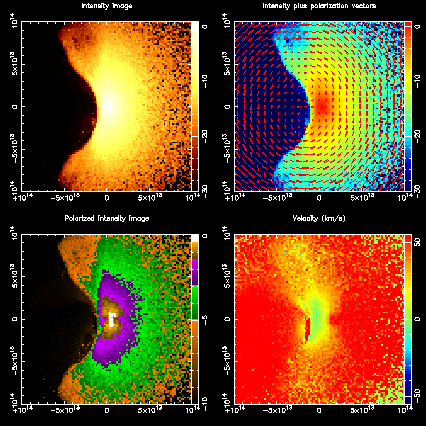 |
The image to the left is a link to a movie of a simulation of
Raman-scattering in a symbiotic binary. The panels are (clockwise,
from top left) the intensity image, the intensity image + polarization
vectors, the velocity image, and the polarized intensity. |
|